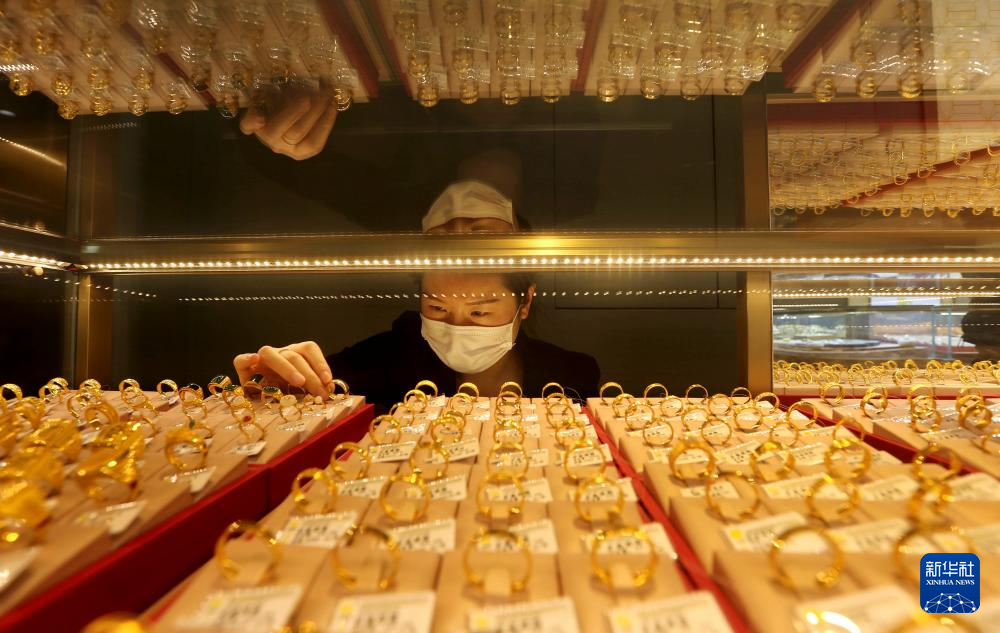
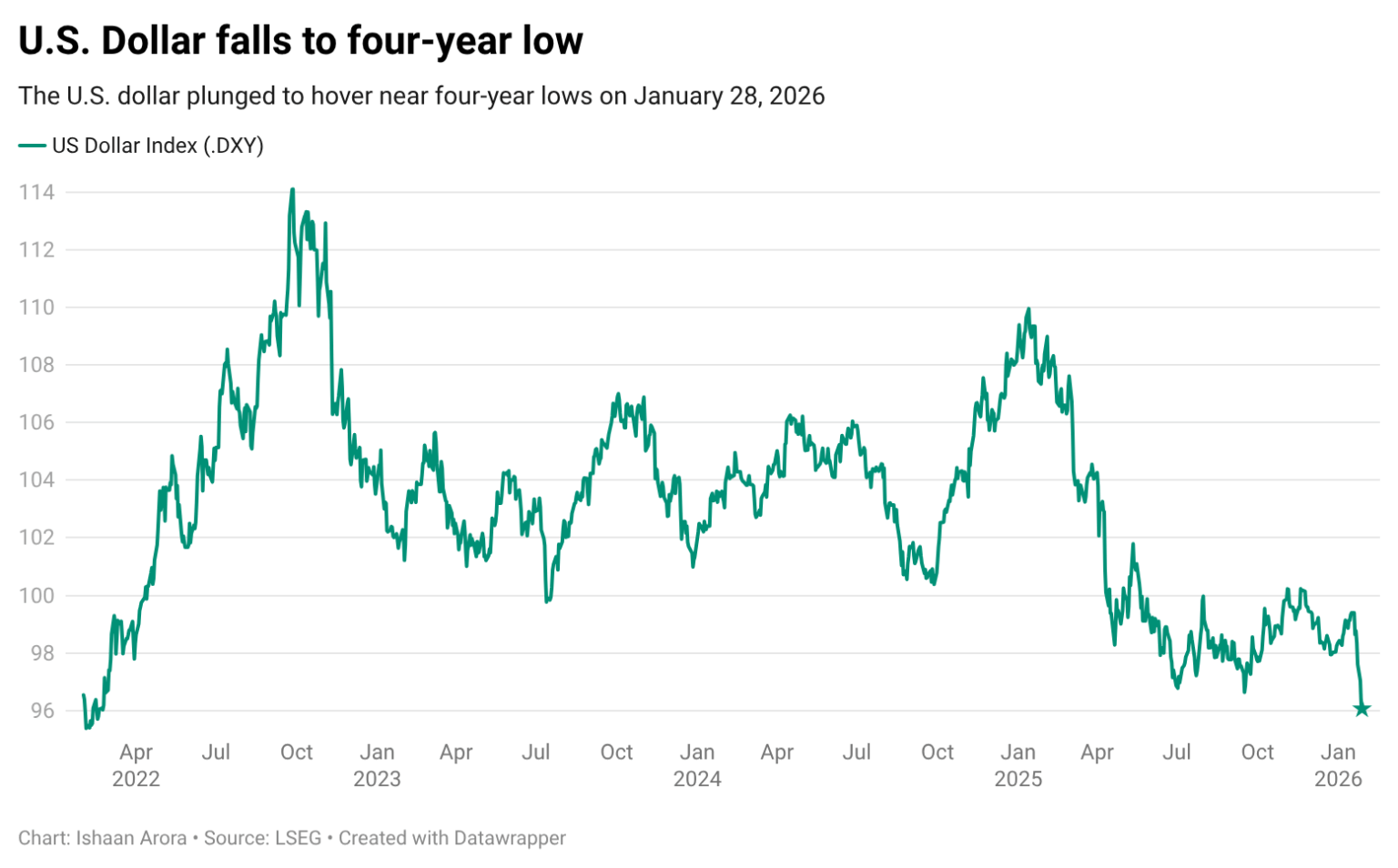
On Wednesday evening, international gold prices broke through the $5,500 per ounce mark, with spot gold rising 2% to a historic high of $5,588.36 per ounce, bringing the cumulative gain for the week to nearly 9%. Since the beginning of this year, gold prices have increased by approximately 20%, far surpassing the full-year growth of … Read More “Gold Soared Past $5,500, Silver Nears $118 – Metals Surge Amid Dollar Weakness” »
Category: Chemicals&Materials
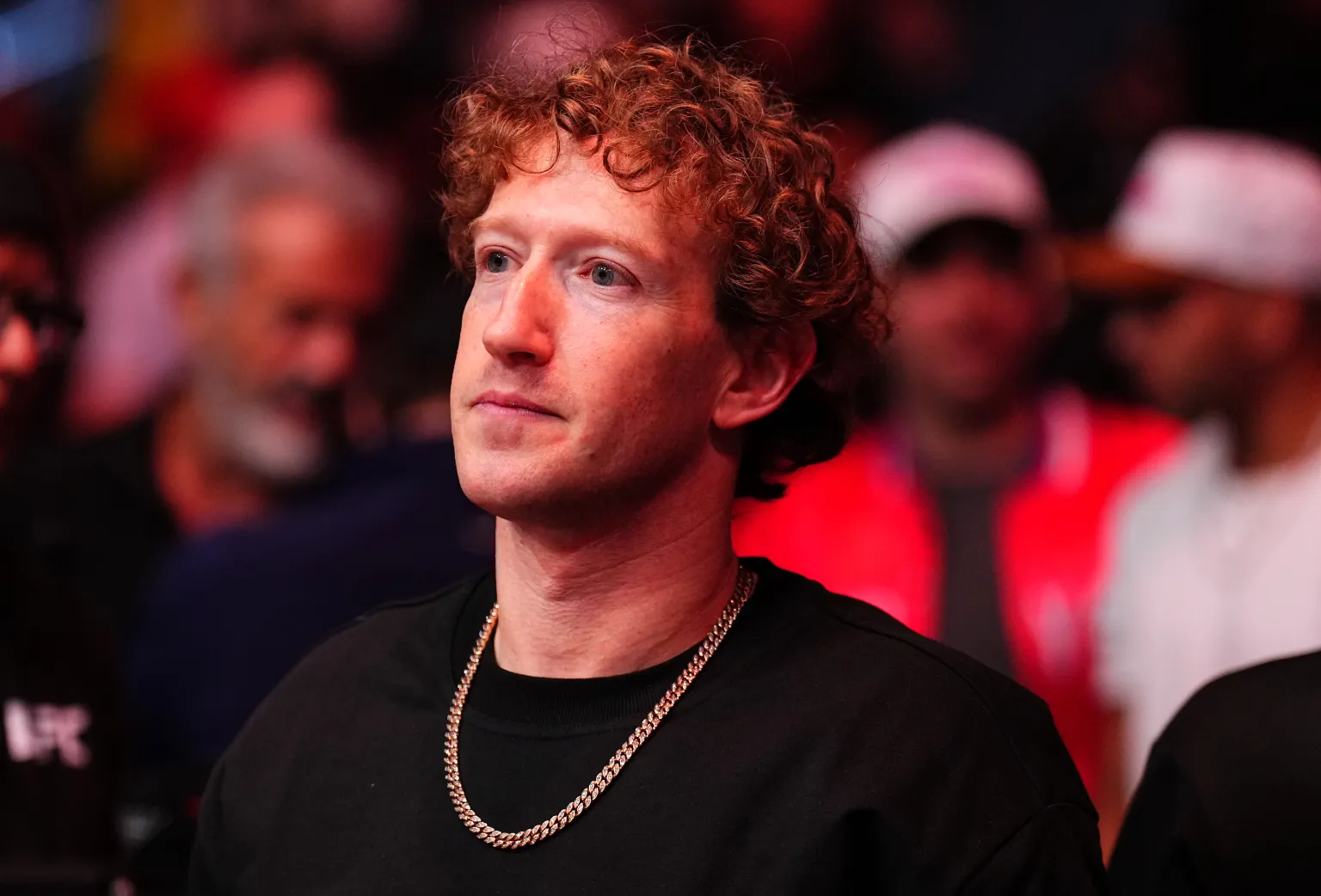
Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg revealed during an investor call on Wednesday that the company will roll out a new generation of AI models and products to users in the coming months. He stated, “In 2025, we rebuilt the foundation of our AI project,” and predicted that “the new year will continue to push the boundaries … Read More “Zuckerberg Vows Major 2026 AI Push, Focused on Commerce with New “Agentic” Tools” »
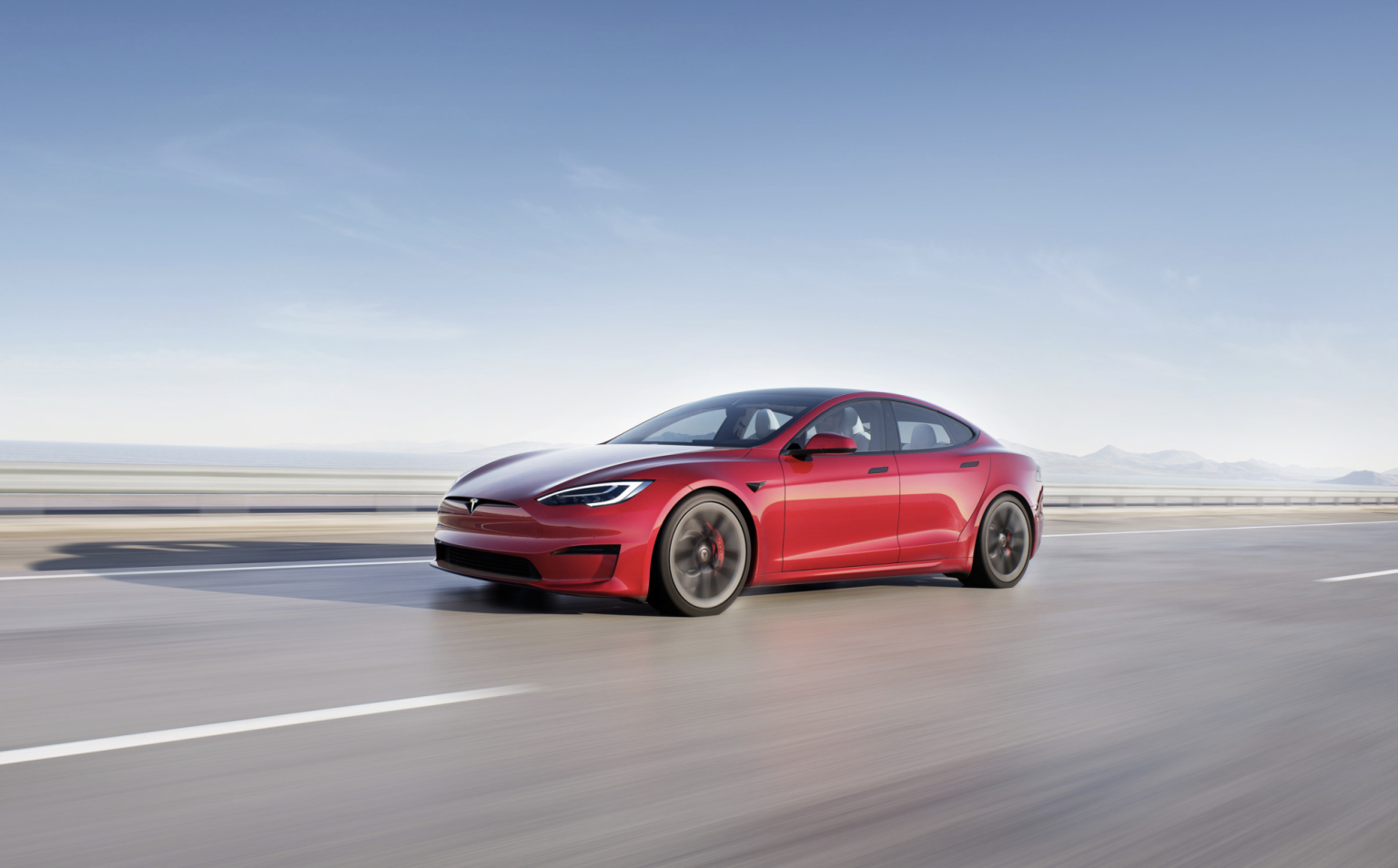
Tesla Announces Gradual Phase-Out of Model S and Model X. CEO Elon Musk stated during the quarterly earnings call that the final versions of these two electric vehicles will be produced next quarter, with future manufacturing resources shifting toward autonomous driving and robotics projects. He emphasized that Tesla will continue to provide long-term support for … Read More “Tesla to Discontinue Model S and Model X Production” »
Google recently upgraded its AI search experience, now allowing users to directly ask follow-up questions from the “AI Overview” on the search results page and seamlessly switch to “AI Mode” for multi-turn, in-depth conversations. (Google Logo) At the same time, the default model for AI Overviews worldwide has been upgraded to the more powerful Gemini … Read More “Google enables seamless transition from AI Overviews to AI Mode” »
The plan covers 35 newly added countries and regions, having been gradually rolled out to dozens of markets since its initial launch in Indonesia last September. The core features of the plan include access to the Gemini 3 Pro and Nano Pro models within the Gemini app, AI video creation through Veo, research and writing … Read More “Google announced that its cost-effective AI Plus plan is now fully available in global markets.” »
Amazon has reached a settlement in a class-action lawsuit alleging the company mishandled customer returns and refunds. The settlement is valued at over $1 billion and includes direct compensation to affected consumers as well as process improvements. (Amazon logo) According to court documents, the agreement stipulates: A cash compensation of $309.5 million to be deposited … Read More “Amazon Reaches Settlement on Returns Process, to Provide Over $1 Billion in Compensation to Consumers” »
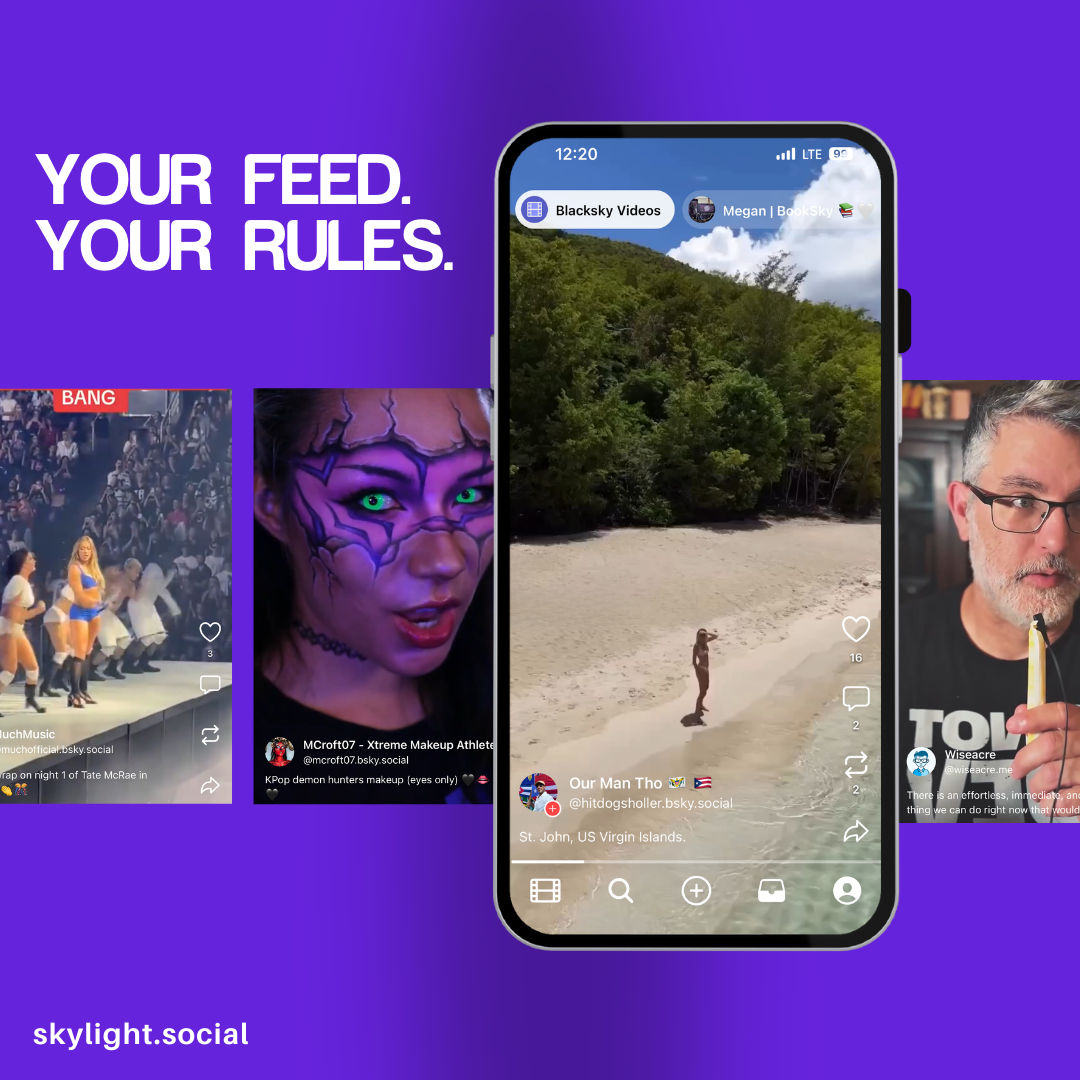
At a time when the ownership change of TikTok’s US business has caused concerns among users, the alternative application Skylight based on open source technology is experiencing rapid growth. This short video application, invested by Mark Cuba and others, and built using a decentralized AT protocol, has recently surpassed 380000 users. (Main Photo Square) The … Read More “With the restructuring of TikTok’s US business, its open-source alternative application Skylight has surpassed 380000 users.” »
Beijing, January 26 (Xinhua) — The international gold market once again reached a historic moment on the 26th, as the New York Mercantile Exchange gold futures price and London spot gold price simultaneously broke through the important threshold of $5100 per ounce during trading, setting a new global gold pricing record. As of the end … Read More “International gold price breaks $5100 per ounce” »
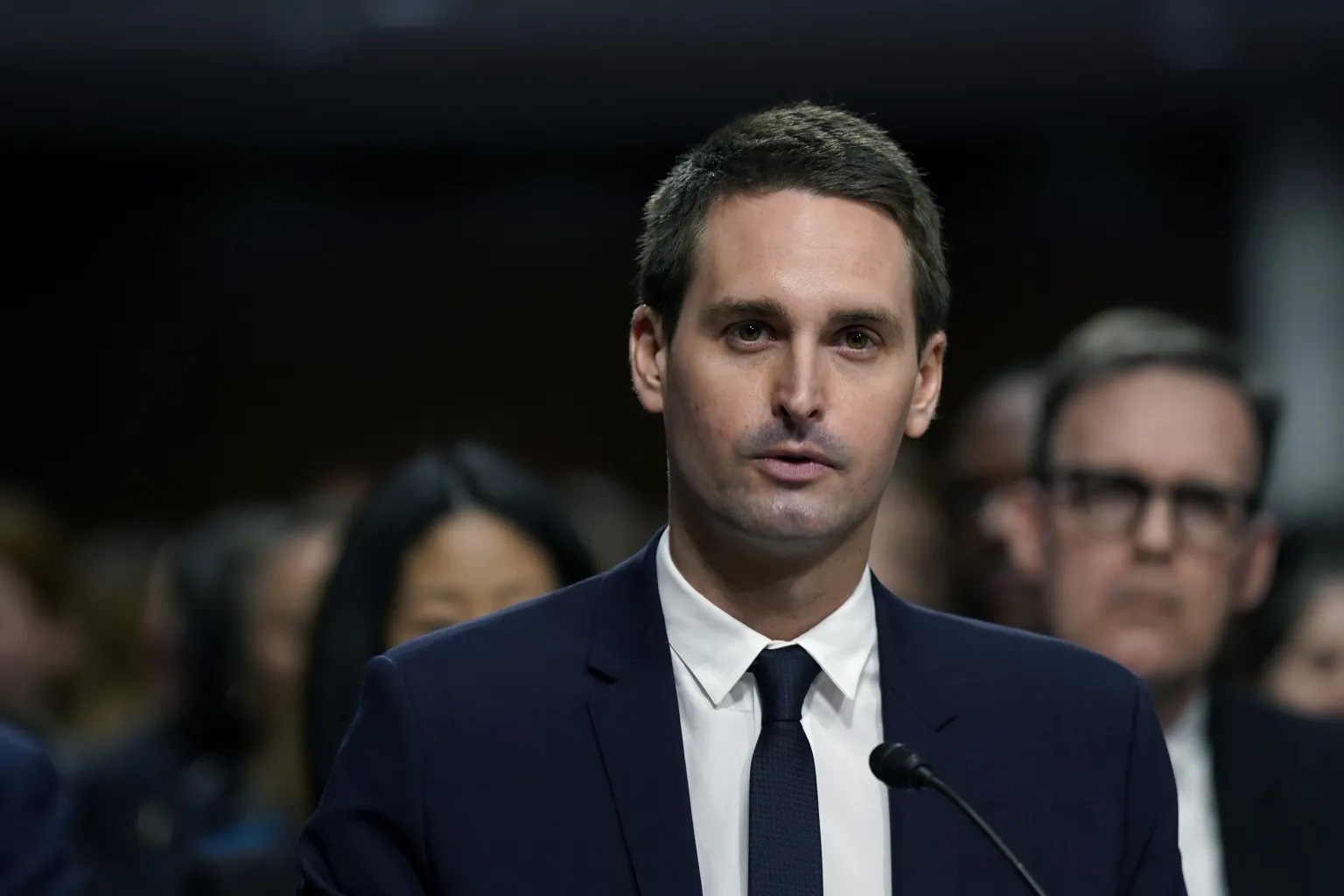
A group of YouTube creators are suing multiple tech giants for illegally capturing their videos to train AI models, and Snap has recently been added to the list of defendants. These three plaintiffs, who collectively have approximately 6.2 million subscribers, accuse Snap of using its video content to train an AI system for in app … Read More “YouTube creator sues Snap accusing its AI model training of copyright infringement” »
Last Saturday, a large number of Gmail users encountered abnormal email system functions, with some users experiencing chaotic email classification and abnormal spam alerts in their inbox. Google subsequently confirmed that the issue had been fully fixed. (gmail icon) According to the official status panel records of Google Workspace, this malfunction began around 5am Pacific … Read More “Google announces fix to Gmail abnormal classification issue” »